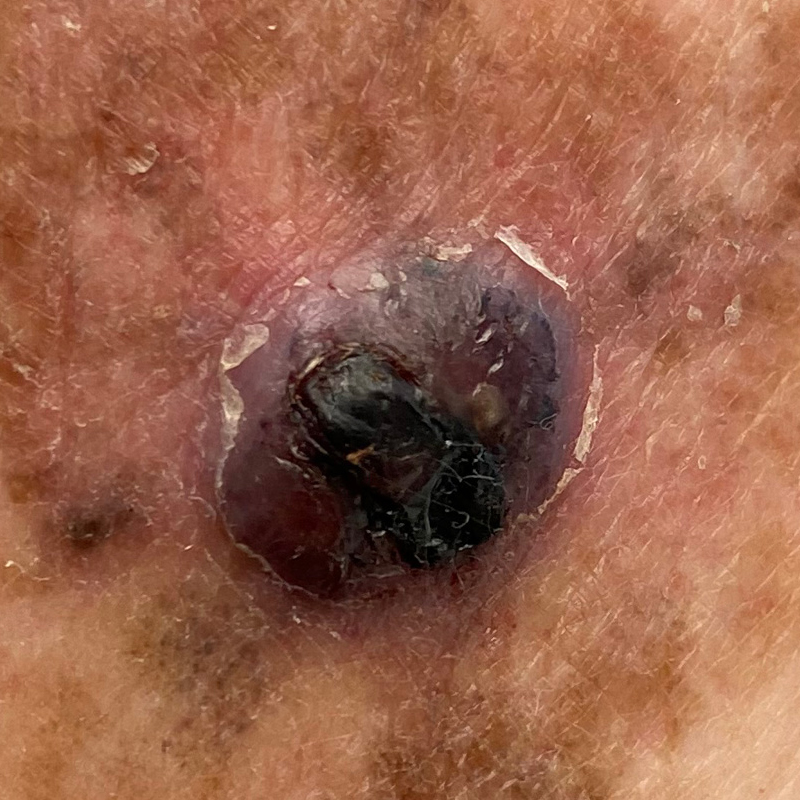
黑色素瘤
Melanoma is a serious type of skin cancer. Melanoma occurs when melanocytes (cells that synthesize pigment which determines skin colour) grows out of control and changes to abnormal cancerous cells. If melanoma is not treated early or not treated, the abnormal cells can spread from the skin to other organs.
Risk
預防
Signs and Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Management

- Risks increasing in people under 40, especially women.
- Fair skin.
- History of severe sunburn.
- Excessive ultraviolet light exposure from the sun or tanning lights.
- Family history of melanoma, have more than 50 moles or more than 5 atypical moles with dark center and a lighter, irregular border.
- Weakened immune system.

- Risks increasing in people under 40, especially women.
- Fair skin.
- History of severe sunburn.
- Excessive ultraviolet light exposure from the sun or tanning lights.
- Family history of melanoma, have more than 50 moles or more than 5 atypical moles with dark center and a lighter, irregular border.
- Weakened immune system.
- Avoid sunlight exposure from 10:00 am to 4:00 pm and tanning lights.
- Wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30.
- Wear protective clothes, long sleeves, long pants, wide-brimmed hats.

- Avoid sunlight exposure from 10:00 am to 4:00 pm and tanning lights.
- Wear sunscreen with at least SPF 30.
- Wear protective clothes, long sleeves, long pants, wide-brimmed hats.

- Mostly develop on face, back, legs, arms that exposes to sunlight.
- Hidden melanomas in soles of feet, palms, fingernail beds and genitals more common in people with darker skin.
- Unusual looking new growth on the skin.
- A change in size, shape, color of an existing mole.
- ABCDE acronym to identify unusual features of melanoma:
- Asymmetry: irregular shape (one half is different from the other half).
- Border: irregular, notched, or scalloped.
- Color: many colors.
- Diameter: > 0.25 inch (> 6mm).
- Evolution: size, colour, or shape can change over time.
- A spot that looks different from all other spots (ugly duckling sign).
- Non-healing sores.
- Redness or new swelling beyond the borders of mole.
- Scaliness, bleeding of mole.
- Itchiness, pain.

- Mostly develop on face, back, legs, arms that exposes to sunlight.
- Hidden melanomas in soles of feet, palms, fingernail beds and genitals more common in people with darker skin.
- Unusual looking new growth on the skin.
- A change in size, shape, color of an existing mole.
- ABCDE acronym to identify unusual features of melanoma:
- Asymmetry: irregular shape (one half is different from the other half).
- Border: irregular, notched, or scalloped.
- Color: many colors.
- Diameter: > 0.25 inch (> 6mm).
- Evolution: size, colour, or shape can change over time.
- A spot that looks different from all other spots (ugly duckling sign).
- Non-healing sores.
- Redness or new swelling beyond the borders of mole.
- Scaliness, bleeding of mole.
- Itchiness, pain.

- Doctor checks the skin all over your body.
- If melanoma is suspected, a biopsy will be performed. A biopsy involves removing a small piece of tissue from the suspected area for microscopic examination of its cells.
- If melanoma is confirmed, melanoma staging will be performed to determine the appropriate treatment. Staging of the disease will inform the doctor about the depth and spread of the melanoma.

- Doctor checks the skin all over your body.
- If melanoma is suspected, a biopsy will be performed. A biopsy involves removing a small piece of tissue from the suspected area for microscopic examination of its cells.
- If melanoma is confirmed, melanoma staging will be performed to determine the appropriate treatment. Staging of the disease will inform the doctor about the depth and spread of the melanoma.

- Surgery: Wide Local excision to remove the melanoma cancer.
- Immunotherapy: Use of medicine that targets the body’s immune system to stop cancer growth.
- Targeted therapy: Melanomas may involve gene changes. Targeted therapy includes medicines that target those gene changes.
- Radiation therapy: Use of radiation to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Use of medicines to kill cancer cells or stop the growth of cancer cells.

- Surgery: Wide Local excision to remove the melanoma cancer.
- Immunotherapy: Use of medicine that targets the body’s immune system to stop cancer growth.
- Targeted therapy: Melanomas may involve gene changes. Targeted therapy includes medicines that target those gene changes.
- Radiation therapy: Use of radiation to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Use of medicines to kill cancer cells or stop the growth of cancer cells.

- Follow up appointments with the doctor periodically to check for melanoma recurrence or new melanomas.
- Check the skin every month to monitor for any changes. A tip is to have assistance from someone you trust to check parts of your body that may be hard to see. If notice any skin changes with existing moles or birthmarks or appearance of new moles, immediately make an appointment with the doctor.
- More treatments may be needed for melanoma recurrence.

- Follow up appointments with the doctor periodically to check for melanoma recurrence or new melanomas.
- Check the skin every month to monitor for any changes. A tip is to have assistance from someone you trust to check parts of your body that may be hard to see. If notice any skin changes with existing moles or birthmarks or appearance of new moles, immediately make an appointment with the doctor.
- More treatments may be needed for melanoma recurrence.